- May 24, 2023
- VPS
- 18866
Share this post on:

Do you know that website loading time can affect your business to a greater extent? Speed is one of the crucial factors in retaining customers and enhancing conversion rates. A survey says that most internet users leave websites if the loading speed is less. This survey solely is enough to show the importance of loading speed.
Website Load Time: Website load time refers to how quickly a website appears when requested by a user. It depends on various factors, such as the complexity of the HTML code used to build the website, image sizes, JavaScript or CSS file count, third-party plugins or widgets, network conditions, device specifications, and browser cache status. Generally, faster-loading sites create better UX and promote user engagement and conversion rate.
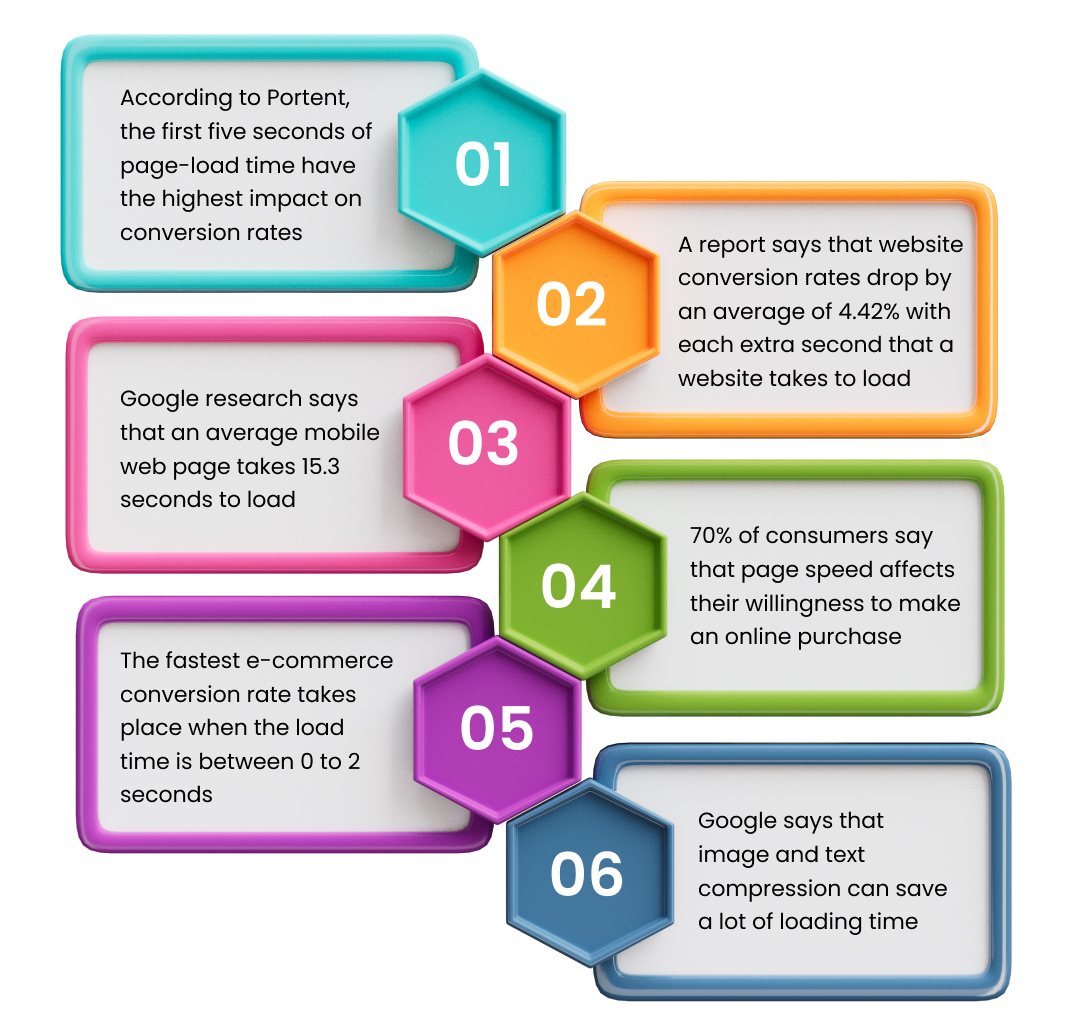
Lets us see what statistics have to say about page load time.
Impact of VPS server on website loading speed
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a web hosting package that splits the physical servers into virtual servers and impacts website loading speed. Instead of running applications directly from a local machine, they run inside virtual environments that offer greater control than traditional shared hosting plans while staying cost-effective.
VPS allows customizing server settings as per business requirements. For instance, you can install preferred operating systems, PHP versions, firewalls, databases, etc. Moreover, since you are not sharing system resources with hundreds of clients, there is no direct impact on performance if there is excessive traffic.
Also, the limited server resources used in VPSs restrict a website's ability to handle high traffic volumes smoothly without causing delays or crashes.
Therefore, VPS servers should be monitored and upgraded regularly, whenever necessary, to accommodate increased visitor demand and ensure optimal website experiences.
Additionally, caching mechanisms like a Content Delivery Network (CDN) help in the distribution of static assets across multiple locations globally. It helps reduce latency issues generated by geographic distance barriers. Optimizing images and code also contributes positively to improving website performance for users accessing pages via VPS servers.
Speed comparison
Here are some quick notes summarizing the comparison between Shared Hosting and VPS regarding speed:
- Shared Hosting and VPS, both types of hosting, have the potential to provide fast page load speeds for website visitors.
- Shared hosting has advantages for smaller and simpler websites with basic needs. However, websites hosted on VPS often have better performance.
- Numerous factors affect website speed beyond just host providers and server configuration.
- Planning and optimization strategies must be implemented before assuming one option supersedes another in terms of overall speed.
- Continuously monitoring resource usage while fine-tuning configurations helps maintain good performance regardless of chosen hosting setup.
The main difference that leads to a different speed of performance depends on the isolated pool of system resources.
Let us consider two scenarios:
Scenario 1: Low Load
When shared and VPS servers have a low load, all accounts present on these servers experience low traffic. Due to this, it is easy to manage the load, so performance does not differ much.
Scenario 2: High Load
In scenarios where the load is high on shared and VPS servers, the traffic flows increase, and users can experience uneven performance and downtime. But due to dedicated scenarios, the performance on VPS stays consistent.
Several Ways to Improve Website Loading Speed
Here are a few ways that can help you improve your website's loading speed.
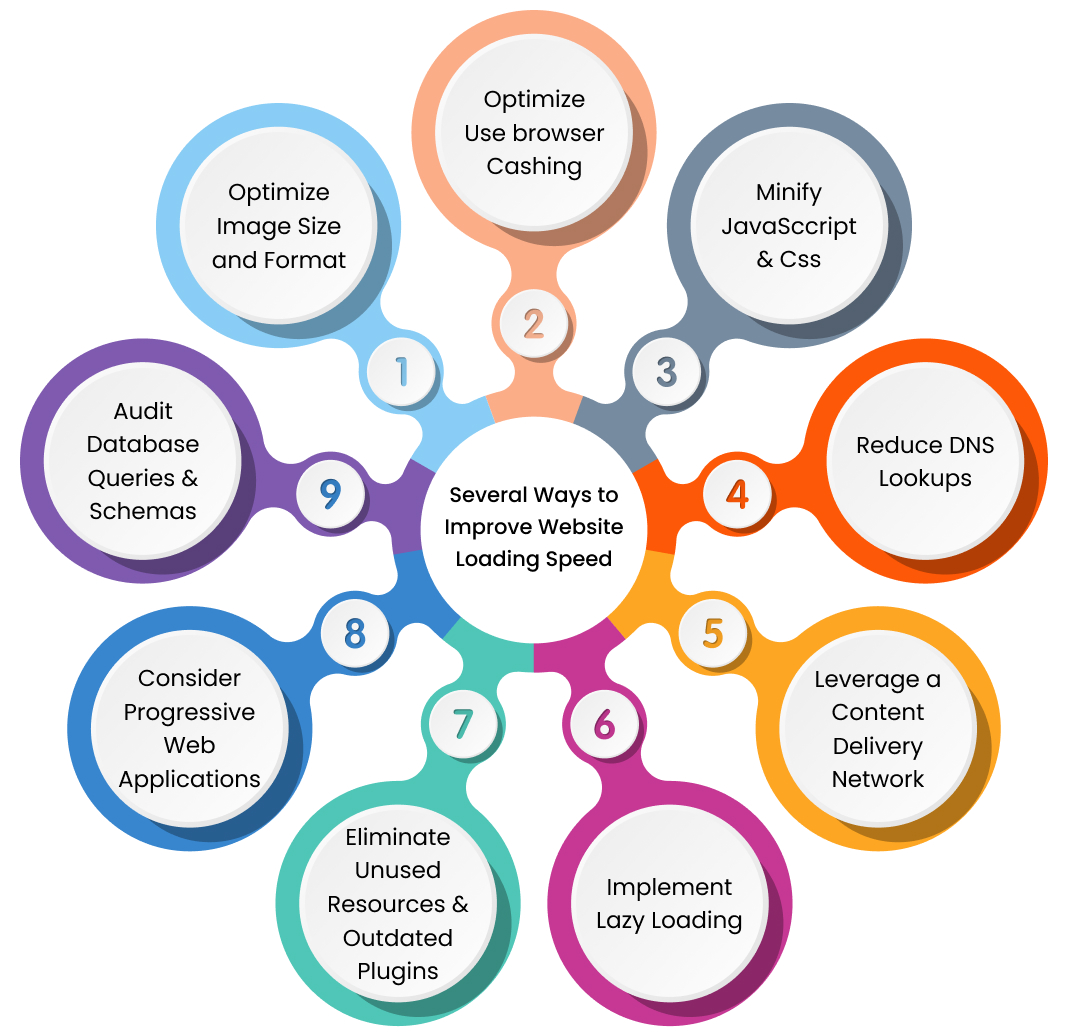
- Optimize Image Size and Format: Large, unoptimized images significantly slow down websites. Use tools such as Photoshop, GIMP, ImageOptim, TinyPNG, JPEGmini, Kraken.io, etc., to compress images while retaining quality. Also, choose formats wisely; JPG, WebP, SVG, PNG, BMP, etc., each has different advantages and disadvantages for specific situations.
- Optimize Use Browser Cashing: Browser caching stores web files locally on the user’s device, allowing them to access the information faster. This reduces the amount of data sent and received each time someone loads a page. You can implement expiration policies and cache validation techniques to minimize conflicts between local and remote versions of cached items.
- Minify JavaScript and CSS: Minification removes unnecessary white spaces, comments, and formatting, reduces file sizes, and improves download speeds. It is advisable to use online tools or build automated processes into your development workflows using Grunt, Gulp, etc.
- Reduce DNS lookups: The number of unique domains liked on your site is directly correlated with DNS lookups, which in turn increases time. Instead, inline images, use a CDN to serve external content, aggregate scripts into one file rather than separate requests, etc. Combine common components across pages to decrease the number of distinct connections required.
- Leverage a Content Delivery Network (CDN): It is a distributed network of edge servers that allows you to access web content quickly and reduces roundtrip latencies that improve speed. Many reputable CDN providers include Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront, Google Cloud CDN, Microsoft Azure CDN, etc.
- Implement lazy loading: Lazy loading is a simple concept for loading ads. By implementing lazy loading, the ads get loaded when the viewers are most likely to see them. Lazy loading plugins exist for the most popular CMS platforms, including WordPress, Magento, Joomla, Drupal, Shopware, OpenCart, PrestaShop, BigCommerce, etc.
- Eliminate Unused Resources and Outdated Plugins: Regularly review code snippets to identify functionalities that are no longer relevant or serve a core purpose. Removing deadweight simplifies maintenance workloads, streamlines update, and keeps applications running smoothly at optimal levels. Disabling unnecessary extensions also reduces resource consumption for increased speed.
- Consider Progressive Web Applications (PWAs): Leverage modern web technologies like service workers, push notifications, and caching to create app-like experiences. It delivers improved offline capabilities, instant reloading, shorter load times, and engagement through simplified discovery and reduced friction. Well-designed PWAs should not require native app installation.
- Audit Database Queries and Schemas: Analyzing SQL statements and ensuring tables follow normalization rules help optimize query execution plans. Not only that, it also decreases join operations, prevents redundancy, and reduces the memory footprint for storage containers. Regular indexing and vacuuming on MySQL or other DBMS platforms can also contribute positively towards enhanced efficiency. Also, it is great to move larger archives or infrequently accessed material to separate tables.
How to Measure Page Speed?
There are several methods to measure page speed, but here are some commonly used ones:
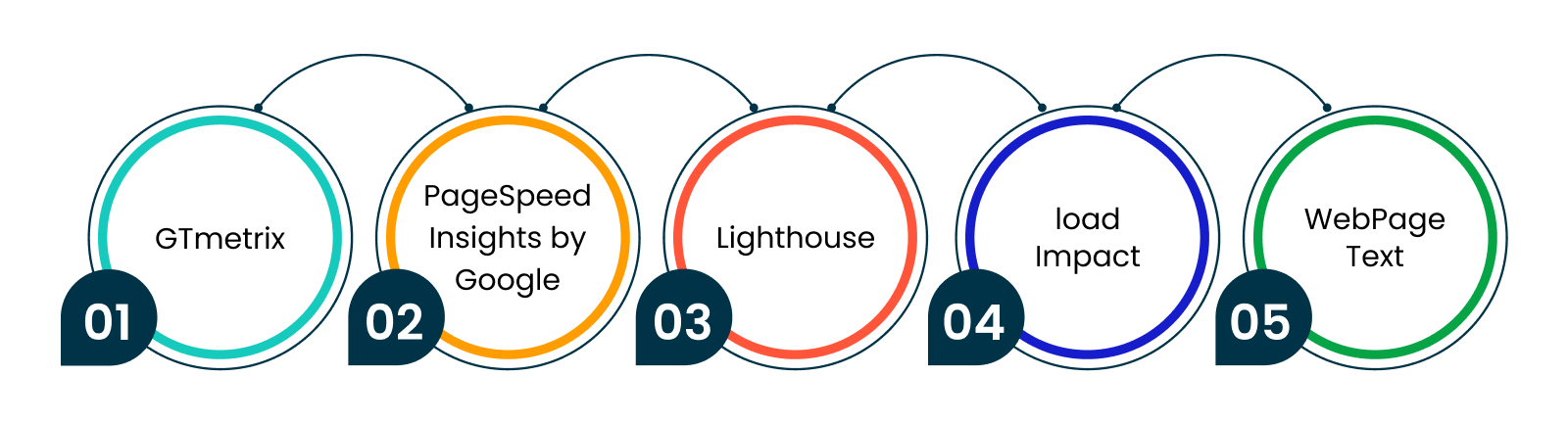
- GTmetrix: This tool offers a comprehensive analysis of a website's performance and identifies opportunities to optimize its speed for desktop and mobile devices. It includes recommendations that can fix technical issues and suggest techniques to enhance page speed. The report helps track progress over time, providing insights and statistics about how well your website performs under real-world conditions.
- PageSpeed Insights by Google: This service analyzes the performance of any URL, generating a report that shows all the factors affecting site speed and recommending optimization techniques to increase it. It offers information on mobile and desktop versions, highlighting areas needing improvement so developers can take action for better performance.
- Lighthouse: A Google tool integrated with Chrome DevTools, that measures the quality of web pages, device configurations, and networks. You can run Lighthouse from the command line or directly inside your browser. It allows you to test variations or compare different URLs for side-by-side comparison.
- Load Impact: Load Impact is a cloud-based performance testing platform. It enables simulated traffic to copy realistic user behavior to analyze system response during peak loads. Its reporting features show page load metrics under different scenarios, such as user concurrency, locations, and hardware configurations. You can use these reports to improve infrastructure scalability and plan future capacity needs accurately.
- WebPageTest: An open-source project offering advanced features to measure page speed, including multi-browser support, network requests analysis, and detailed waterfall charts representing loading sequence breakdowns. It integrates with CDN providers, making it possible to monitor real end-user connections by fetching samples from diverse regions around the globe. With flexible options such as custom domains, user agents, and settings, WebPageTest helps evaluate website performance effectively in dynamic environments.
Reasons why website speed matters
Website speed has become increasingly important as more consumers access websites using their mobile devices and high-speed internet connections. However, many businesses still underestimate the importance of page load time. This can lead to serious consequences for their online presence, customer satisfaction, and even revenue.
Here are the reasons why the speed of your website matters.
- Lower Bounce Rate: Bounces decrease due to improved website performances, engagement levels increase, driving return visits, conversions, and higher revenues.
- Improved Search Engine Rankings: Websites with optimized speeds have seen improved search engine ranking. They can attract more relevant traffic and help customers find products/services easily online.
- Enhanced User Experience: Faster-loading websites give better user experiences by reducing wait times, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Fast-loading websites consume fewer server resources than those running slowly. Hence owners save money on expensive infrastructure and maintenance expenses.
- Greater Customer Retention: When sites perform well, users become confident interacting with them. Consequently, businesses see increased customer loyalty/repeat purchases, making marketing campaigns more effective in the long run.
- Mobile Optimization: Since mobile usage has surpassed desktop browsing these days, having great speed provides seamless mobile experiences and ensures wider reach, keeping your company competitive.
- Better Brand Image: When visitors perceive brands positively based on site performance alone, they can help businesses create leads through referrals and word-of-mouth promotion.
- Secure User Data: With faster responses, sensitive transactions like credit card details can be processed securely online with minimal risk of exposure to hacking attempts.
- Time Management: A good speed saves users time. Moreover, customers want to get more information in a limited time. So high speed saves valuable minutes and benefits everyone involved.
To Conclude:
Finally, achieving optimal website speed requires constant monitoring and tuning but helps companies enhance their sales rate. Not only that, a seamless website offers a great user experience and retains customers. Hence, website administrators must always prioritize speed improvements as essential objectives while managing their online presence.
If you are looking for the most reliable managed services, contact jiWebHosting. We offer the most secure and fast-managed VPS services that help you grow your business.